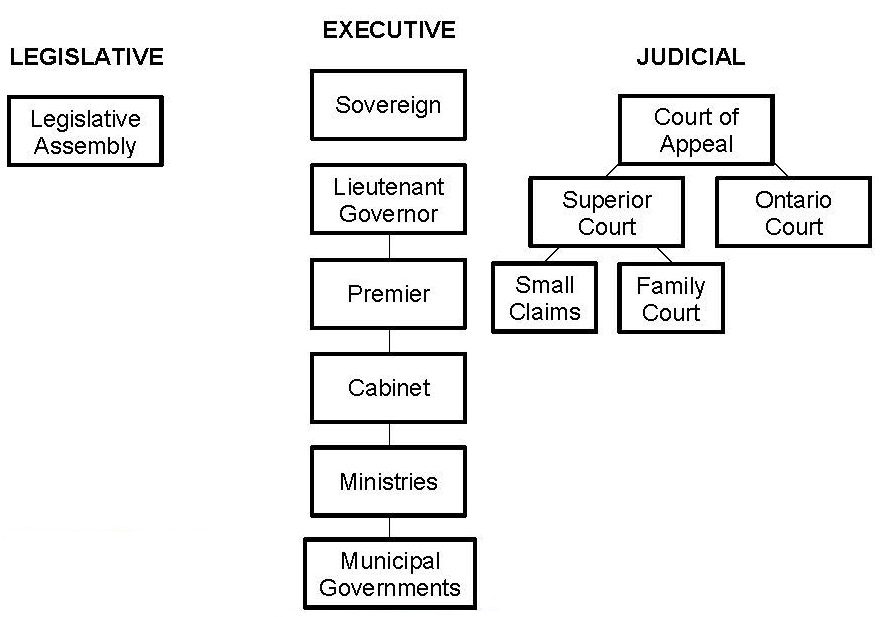
Provincial government in Canada is responsible for property and civil rights, administration of justice, natural resources and the environment, education, health, and welfare. Each province's government structure may be slightly different from each other, but the fundamentals are identified in the chart below. The main differences are:
- in the legislative branch, just one house instead of two (styled the Legislative Assembly, House of Assembly, or National Assembly, depending on the province);
- in the executive branch, different names for the Provincial Heads of State (Lieutenant Governor instead of Governor General) and Heads of Government (Premier instead of Prime Minister); and
- in the judicial branch, various court structures for each province (the Ontario court structure is the one shown below).
|



